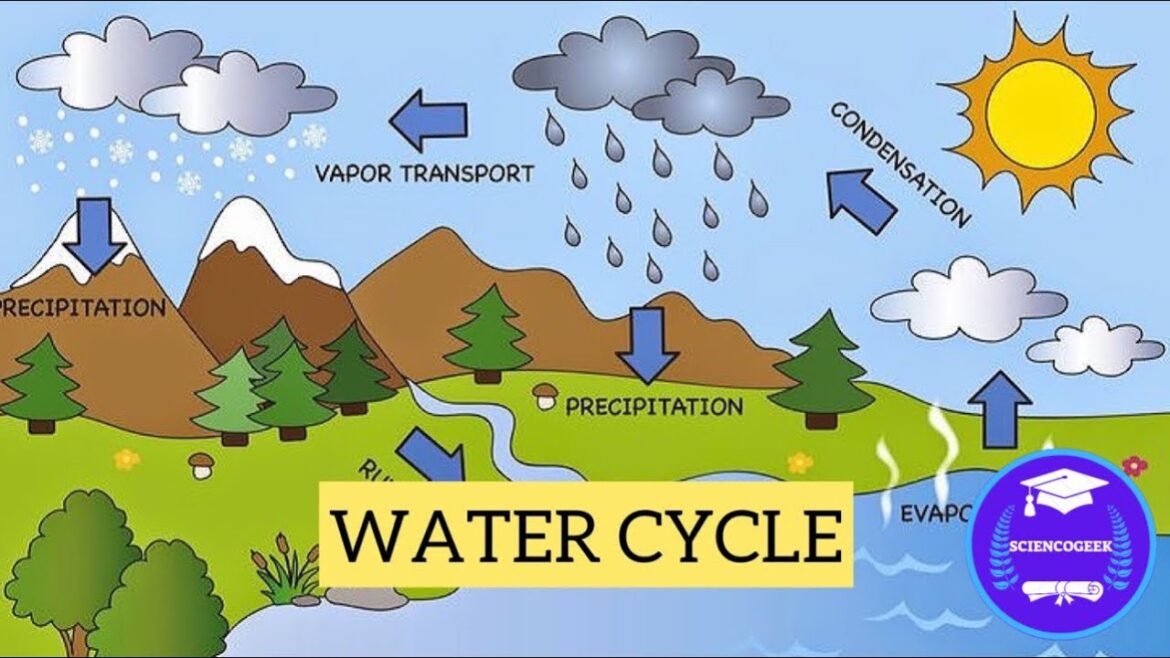
The 6th Grade:Nzc130ce_I0= Water Cycle is essential for our planet, constantly recycling water and supporting all life. It consists of three main stages: evaporation, condensation, and precipitation. You see evaporation when water turns into vapor, often on sunny days. As this vapor cools in the atmosphere, it forms clouds through condensation. Eventually, the water falls back to Earth as precipitation, like rain or snow. This cycle not only shapes weather patterns but also affects ecosystems and water availability. Understanding more about each part of the cycle can help you appreciate how interconnected everything is. Discover more about its impact on our world!
Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 Understanding the 6th Grade:Nzc130ce_I0= Water Cycle
- 3 Stages of the Water Cycle
- 4 Importance of Evaporation
- 5 Role of Condensation
- 6 Precipitation Explained
- 7 Impact on Climate
- 8 Water Cycle and Ecosystems
- 9 Conserving Water Resources
- 10 Frequently Asked Questions – 6th Grade:Nzc130ce_I0= Water Cycle
- 11 Conclusion – 6th Grade:Nzc130ce_I0= Water Cycle
Key Takeaways
- The 6th Grade:Nzc130ce_I0= Water Cycle consists of three main stages: evaporation, condensation, and precipitation, crucial for maintaining Earth’s ecosystems.
- Evaporation turns liquid water into vapor, influenced by heat, wind, and surface area.
- Condensation forms clouds and moisture droplets when air cools, impacting weather patterns.
- Precipitation returns water to the surface as rain, snow, or hail, essential for rivers and lakes.
- Sustainable practices, like efficient irrigation and rainwater collection, help conserve water resources and support the water cycle.
Understanding the 6th Grade:Nzc130ce_I0= Water Cycle
As you explore the intricate processes of the water cycle, you’ll discover how essential this natural phenomenon is to sustaining life on Earth. The cycle not only regulates water availability but also plays a crucial role in addressing issues like water scarcity and climate change. Understanding how water moves through the environment helps you appreciate the importance of groundwater recharge and effective watershed management.
Urban runoff can disrupt this cycle, leading to aquifer depletion and decreased moisture retention in soils. By implementing sustainable irrigation practices, you can contribute to a healthier water cycle that supports both agricultural productivity and ecosystem health.
When you consider the impacts of climate change, it’s clear that the water cycle is under stress. Increased evaporation rates and altered precipitation patterns can exacerbate water scarcity, highlighting the need for responsible water management. Your awareness of these interconnected processes empowers you to advocate for practices that minimize urban runoff and protect crucial water resources. By understanding the water cycle, you’re better equipped to make choices that promote sustainability and freedom for future generations.
Stages of the Water Cycle
Now that you understand the water cycle, let’s explore its stages. First up is evaporation, where water transforms into vapor and rises into the atmosphere. Then, we’ll look at the various types of precipitation that return moisture back to the Earth.
Evaporation Process Explained
The evaporation process is a significant stage in the water cycle, where liquid water transforms into vapor and ascends into the atmosphere. This remarkable transformation is influenced by several evaporation factors, including temperature, humidity, wind speed, and surface area. Understanding these factors helps you appreciate how water interacts with the environment.
- Heat from the sun accelerates evaporation.
- Higher wind speeds enhance water vapor dispersal.
- Lower humidity levels allow more water to evaporate.
- Larger surface areas increase evaporation rates.
- Water bodies like lakes and oceans are primary sources of vapor.
You can see evaporation in action in various applications. For instance, it plays an important role in weather patterns and agriculture. In gardening, knowing when to water your plants can help you account for evaporation, ensuring your plants receive enough moisture. Additionally, evaporation is fundamental in cooling processes, such as sweat evaporating from your skin, which helps regulate body temperature. By recognizing these evaporation factors and applications, you gain insights into the water cycle, empowering you to appreciate the natural world and the freedom it provides.
Precipitation Types Overview
Precipitation plays an essential role in the water cycle, delivering fresh water back to the Earth’s surface in various forms. Understanding the different types of precipitation helps you appreciate the complexity of nature and its impact on your environment. Here’s a quick overview:
| Type of Precipitation | Characteristics | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| Rain | Liquid water droplets | Rain gauge (in mm) |
| Snow | Ice crystals | Snow ruler (in inches) |
| Hail | Ice pellets | Weight (grams) |
| Fog | Water vapor in the air | Dew point temperature |
Each type has unique features. Rainfall measurement tells how much water falls in a specific area, while snow accumulation reveals winter’s impact. Hail formation occurs during thunderstorm conditions, bringing sudden bursts of ice. Fog development, on the other hand, creates a mystical atmosphere but is significant for local ecosystems. Recognizing these elements helps you understand how weather patterns affect your daily life and the environment around you. So, the next time you experience precipitation, remember its essential role in maintaining the water cycle!
Importance of Evaporation
Evaporation plays an essential role in the water cycle, acting as a natural engine that drives the movement of water from the Earth’s surface into the atmosphere. This process isn’t just fascinating; it’s critical for life as we understand it. Understanding the evaporation significance can help you appreciate the world around you.
- It helps regulate temperature by cooling the surface.
- Plants rely on it to transport nutrients from the soil.
- It contributes to the formation of clouds and subsequent precipitation.
- Evaporation can be observed in everyday life, like puddles drying up after rain.
- It’s fundamental for maintaining ecosystems, from wetlands to deserts.
When you think of evaporation examples, consider how it affects your daily life—whether it’s the steam rising from a hot cup of coffee or the way a wet towel dries in the sun. Each instance highlights the importance of this process. Without evaporation, our planet wouldn’t have the balanced climate and water supply necessary for thriving ecosystems. So next time you see water disappearing into thin air, remember its essential role in our ever-revolving water cycle!
Role of Condensation
Condensation is an essential process in the water cycle, transforming water vapor back into liquid form and playing a key role in weather patterns and the distribution of water on our planet. You might not realize it, but every time you see dew on grass or fog in the morning, you’re witnessing the condensation process in action. This transformation occurs when atmospheric moisture cools, allowing water vapor to clump together and form tiny droplets.
Here’s a quick overview of how condensation affects our environment:
| Process | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Air | When air cools, it can’t hold as much moisture. | Initiates condensation. |
| Droplet Formation | Water vapor condenses into tiny water droplets. | Creates clouds, fog, or dew. |
| Weather Patterns | Condensed moisture can lead to precipitation. | Influences local and global climates. |
Understanding the role of condensation helps you appreciate how interconnected our climate systems are. Without it, we’d struggle to maintain the balance of water we need for life. So next time you notice fog or dew, remember the essential role condensation plays in our water cycle!
Precipitation Explained
Once water droplets have formed through condensation, they’re ready to take the next step in the water cycle: precipitation. This process is essential for maintaining the hydrological balance on Earth. When humidity levels rise and atmospheric pressure changes, you’ll notice cloud development intensifying. Eventually, these clouds become heavy with moisture, leading to various forms of precipitation like rain, snow, sleet, or hail.
Here are some key aspects of precipitation to keep in mind:
- Rain formation occurs when droplets combine and grow large enough to fall.
- Weather patterns can shift dramatically due to storm systems, affecting where and how much precipitation occurs.
- Seasonal variations can determine the type of precipitation you experience—think of summer thunderstorms versus winter snow.
- Urban runoff can impact water quality, as rainwater collects pollutants from surfaces.
- Understanding atmospheric pressure helps predict when precipitation is likely to occur.
Impact on Climate
The water cycle plays an essential role in regulating our climate, and it’s influenced by greenhouse gas emissions you might not think about. These emissions can alter temperature patterns and change precipitation dynamics, affecting everything from droughts to floods. Understanding this relationship helps you grasp how interconnected our planet’s systems truly are.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas emissions play an essential role in shaping our climate, affecting everything from weather patterns to sea levels. You might be surprised to learn how these emissions influence your everyday life and future. Here are some key points to ponder:
- Human activities are the primary emission sources of greenhouse gases.
- Carbon dioxide and methane are two major contributors to climate change.
- Your carbon footprint can greatly impact the environment.
- Renewable energy sources can help reduce emissions.
- Policy measures are vital for effective mitigation strategies.
As you explore the effects of greenhouse gases, you’ll see how our choices matter. Activities like driving gas-powered cars, using fossil fuels for energy, and deforestation all increase emissions. Shifting to renewable energy sources like solar and wind can help mitigate these effects. Additionally, adopting better policies can guide communities towards sustainable practices.
Taking action now is essential to curb climate change. By understanding the impact of your decisions and supporting efforts that promote sustainability, you can contribute to a healthier planet. Together, we can create a future where cleaner air and a stable climate are within reach.
Temperature Regulation Effects
Understanding greenhouse gas emissions helps clarify how temperature regulation affects our climate. When these gases accumulate in the atmosphere, they lead to temperature fluctuations that can disrupt natural patterns. You might notice that warmer temperatures can amplify the water cycle, resulting in more evaporation and, eventually, heavier rainfall. This creates a cycle of climate feedback that can be both beneficial and harmful.
As temperatures rise, the earth’s surface warms, causing ice caps and glaciers to melt. This not only contributes to rising sea levels but also alters local and global climates. You may find that regions once known for their stable climates begin experiencing unpredictable weather patterns, making it difficult for ecosystems and communities to adapt.
Moreover, temperature regulation plays an essential role in the balance of our environment. Warmer conditions can lead to increased humidity, affecting everything from agriculture to wildlife. By understanding these temperature effects, you’re better equipped to recognize the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and advocating for changes that protect our planet. Every small effort counts in maintaining a stable climate for future generations.
Precipitation Patterns Influence
Precipitation patterns markedly shape our climate, influencing everything from local ecosystems to global weather systems. Understanding these patterns can help you grasp the intricate balance of our environment and its impact on daily life.
- Drought patterns can lead to water scarcity.
- Urban runoff affects water quality and increases pollution effects.
- Seasonal variations dictate agricultural impacts, influencing crop yields.
- Different climate zones experience unique precipitation patterns.
- Changes in rainfall can escalate flood risks and cause habitat changes.
When you look at how precipitation interacts with atmospheric conditions, it becomes clear that these patterns don’t just affect weather; they shape entire ecosystems. For instance, prolonged drought patterns can devastate agriculture, reducing food supplies and altering landscapes. Conversely, excessive rainfall can lead to urban runoff, where pollutants wash into waterways, harming water quality.
The interplay between seasonal variations and climate zones also plays a significant role. Each zone has adapted to specific precipitation levels, and shifts can disrupt these delicate ecosystems. By recognizing these influences, you can appreciate the importance of sustainable practices to mitigate the adverse effects of changing precipitation patterns.
Water Cycle and Ecosystems
The intricate relationship between the water cycle and ecosystems is fundamental to life on Earth. Every drop of water plays a critical role in maintaining ecosystem balance and ensuring proper water distribution. When you think about it, the journey of water from the sky to the ground and back affects everything around you.
Here’s a quick overview of how different components of the water cycle interact with ecosystems:
| Water Cycle Component | Ecosystem Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporation | Increases humidity | Rainforests thrive |
| Condensation | Forms clouds | Weather patterns |
| Precipitation | Supplies fresh water | Rivers and lakes |
| Infiltration | Replenishes groundwater | Aquifers |
| Transpiration | Affects local climate | Vegetation growth |
As you can see, each step of the water cycle contributes to the overall health of various ecosystems. Without this continuous movement of water, plants, animals, and even humans would struggle to survive. Understanding these connections empowers you to appreciate the beauty of nature and the importance of protecting our water resources.
Conserving Water Resources
Saving water is essential for sustaining our planet’s ecosystems and ensuring that future generations have access to this important resource. By adopting water conservation methods, you can play a significant role in preserving this critical resource. Here are some effective strategies you can implement:
- Practice efficient irrigation techniques to minimize waste.
- Collect rainwater for gardening and household use.
- Recycle water whenever possible, such as using greywater systems.
- Stay informed about drought management practices in your area.
- Engage in community awareness and resource education initiatives.
Each small step counts! By embracing sustainable practices, you can greatly reduce your ecological impact. Consider how much water you use daily and identify areas for improvement. Whether it’s fixing leaks, choosing drought-resistant plants, or advocating for policy initiatives aimed at water conservation, your actions matter.
Encouraging others to adopt similar habits creates a ripple effect, amplifying your efforts and fostering a culture of water stewardship. Remember, when you conserve water, you’re not just saving a resource; you’re ensuring a brighter future for all. Let’s work together to protect our water resources!
Frequently Asked Questions – 6th Grade:Nzc130ce_I0= Water Cycle
How Does Human Activity Affect the Water Cycle?
Human activities like urban development and deforestation disrupt the water cycle. Pollution impacts water quality, while climate change alters precipitation patterns. You’re witnessing these changes, affecting ecosystems and your access to clean water.
What Are the Different Types of Precipitation?
When you think about precipitation formation, consider how rain types, like drizzle and thunderstorms, contrast with snow and hail. Each has its own unique process, bringing life and variety to our weather experience.
Can the Water Cycle Change With Seasons?
The water cycle dynamics shift with seasonal variations, affecting evaporation rates, precipitation types, and overall water movement. You’ll notice these changes in your environment, from snow in winter to rain in spring.
How Do Plants Contribute to the Water Cycle?
Plants contribute to the water cycle by absorbing soil moisture and releasing water vapor through transpiration. You’ll see how this process helps maintain humidity, supports weather patterns, and nurtures the ecosystem around you.
What Is Groundwater and Its Role in the Water Cycle?
Groundwater’s essential in the water cycle, acting as a reservoir in aquifers. It helps maintain ecosystems and supports plants. When it rains, groundwater recharge replenishes these sources, ensuring a sustainable water supply for everyone.
Conclusion – 6th Grade:Nzc130ce_I0= Water Cycle
As you look up at the sky, picture the dance of 6th Grade:Nzc130ce_I0= Water Cycle swirling and shimmering in the sunlight, ready to fall as rain. The water cycle isn’t just a process; it’s an essential rhythm that sustains life on Earth. By understanding its stages, you can appreciate the beauty of nature’s design. Let’s cherish and conserve our precious water resources, ensuring that this magical cycle continues to nourish our planet for generations to come.